NorthStar Revenue Security
A innovative approach to detect and address CDN leeching in real-time
Extending Content Provenance to Service Integrity
NorthStar revenue security is EZDRM’s innovative use of provenance tracking for real-time detection and response to illegitimate streams of video leeched from the CDN of a video service operator.
- Offering a real-time mechanism to detect and defeat CDN leeching piracy
- Leverages C2PA and CMCD standard building blocks
- CDN agnostic implementation with low overhead
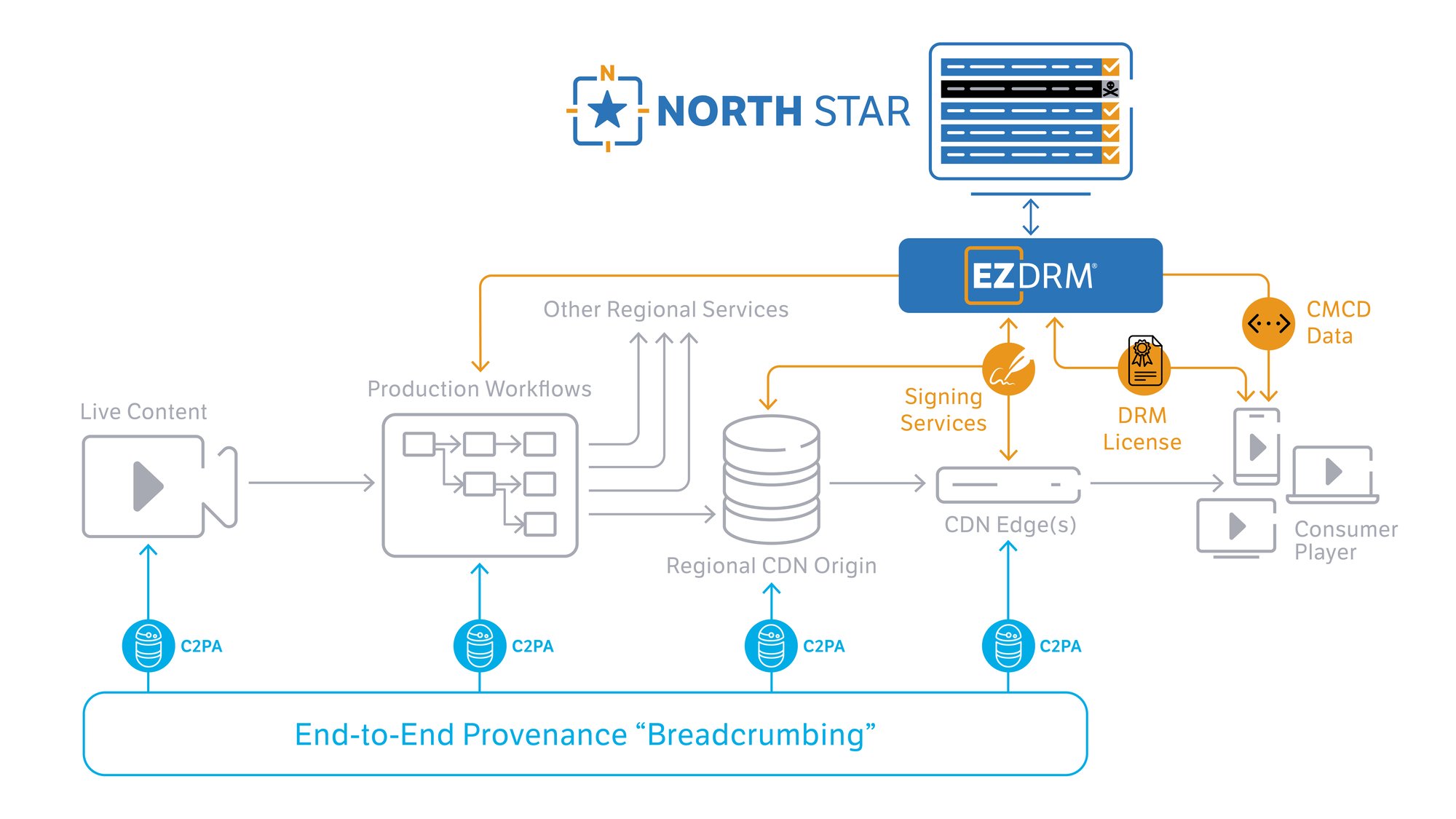
NorthStar revenue security iis EZDRM’s innovative use of provenance tracking for real-time detection and response to illegitimate streams of video leeched from the CDN of a video service operator. Taking full advantage of C2PA (Coalition for Content Provenance and Authenticity) and CMCD (Common Media Client Data) building blocks, EZDRM has dramatically expanded the use cases to address key issues related to content monetization. The NorthStar approach creates a verified “breadcrumb trail” for the actual pattern of content distribution inside and outside a licensed region, allowing service operators and content providers to not only identify but also address rogue CDN hacking attempts as they happen.
CDN leeching has emerged as a new attack vector in the ever-evolving arms race around video service piracy. Unauthenticated users exploit CDN endpoints to gain access to high-quality content streams without permission. These bogus attachment mechanisms are often behind the bundling of pirate video services offered to consumers via increasingly sophisticated services and websites. As the lucrative business of live event delivery moves further and further towards a universe of streaming services, these evolving forms of attack present a big challenge.
The parasitic nature of CDN leeching makes it problematic to detect - the illegitimate users have a service usage signature very similar to those with legitimate rights to view content. Hijacking of a CDN service serves as a very effective entry point for pirates to obtain a high-quality source of content, enabling them to distribute pirated material while hiding behind the legal service at low cost to themselves.
What’s the relevance of C2PA in this context? NorthStar extends the provenance workflow routinely applied to a live content stream by additionally enabling C2PA signed metadata at the service CDN origin (or origins) and at each of the CDN edge nodes through which the stream flows. At each consumer device, standard CMCD instrumentation relays these signatures back to NorthStar. This extended use of CMCD and C2PA gives a full map of the real-time content distribution across CDNs, and inside and outside of a licensed service geography. With a real-time delivery map available, it’s a simple step to identify rogue viewing sessions and shut them down. When integrated with EZDRM’s DRM as a Service solution,rights holders now have a broader range of active tools to combat live service piracy.
While video watermarking has often been proposed as a solution to address pirate streaming service issues, the extended response times for stream capture, analysis and takedown limit the effectiveness of any such approach. Watermarking has also been a commercially ambiguous offering, where the responsibilities of rights holders and service operators do not necessarily align.
Similarly, today’s AI and ML analytics services have been advanced as ways to offer detection and defense against such forms of service attack. But again, capture and analysis processing latency often means only an “after the fact” view of service losses can be seen, not a way to understand and address the issues in real-time.
Implementations of NorthStar are CDN agnostic, and use multi-cloud hosted signature generation in conjunction with the CDN edge nodes. Serverless and stateless C2PA signing is offered as an efficient EZDRM cloud micro-service, taking less than 300 milliseconds to execute. In order to manage bandwidth and cost, only a selectable subset of video stream segments are signed, offering a trade-off between delivery overhead and session shut-down latency.
